
India’s diverse driving conditions and mix of terrains demand the best in reliability, ruggedness, performance, and safety. To meet these demands, the types of batteries for electric vehicles currently proven to be the most suitable and viable as of the early 21st century are LFP (Lithium Ferro Phosphate) and NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt).
Previously, we covered the different types of lithium-ion battery chemistries that make up modern contemporary lithium-ion battery technology. This addition of Battery Decoded aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the types of batteries used in Electric Vehicles in India and describe how these two electric vehicle battery chemistries manage to tick every single box that Indian consumers look out for.
India’s diverse driving conditions and mix of terrains demand the best in reliability, ruggedness, performance, and safety. To meet these demands, the types of batteries for electric vehicles currently proven to be the most suitable and viable as of the early 21st century are LFP (Lithium Ferro Phosphate) and NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt).
Previously, we covered the different types of lithium-ion battery chemistries that make up modern contemporary lithium-ion battery technology. This addition of Battery Decoded aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the types of batteries used in Electric Vehicles in India and describe how these two electric vehicle battery chemistries manage to tick every single box that Indian consumers look out for.
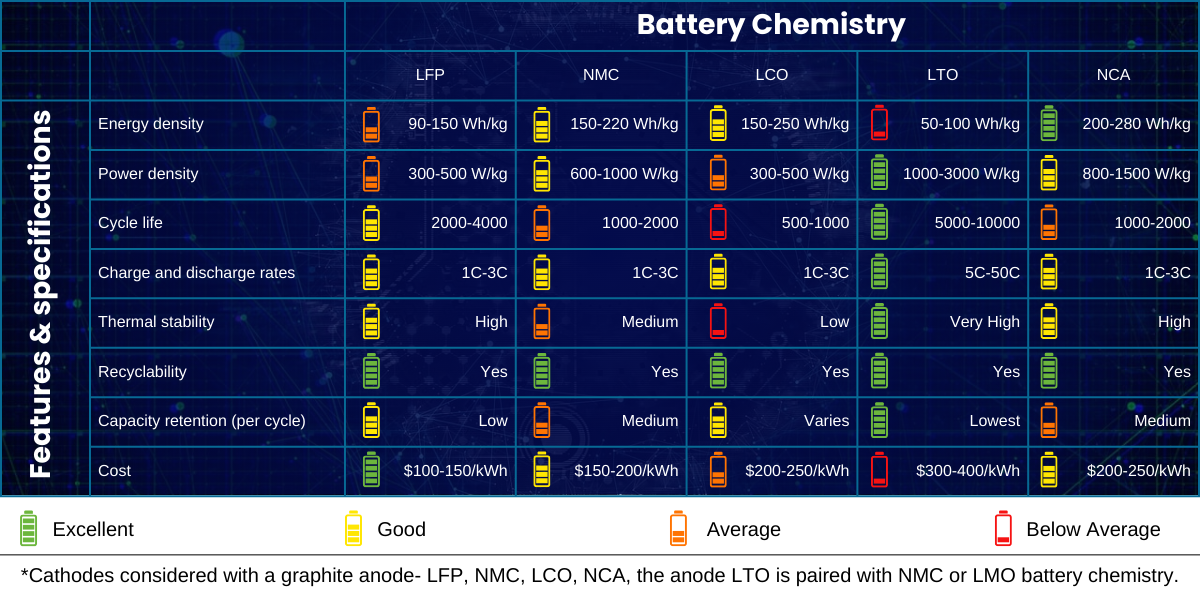
As of the early 2020s, LFP and NMC are by far the two most predominant Li-ion battery chemistries used in Indian EVs. They have gained widespread popularity because of their low cost and high reliability. However, they also have some distinct advantages and disadvantages that make them suitable for different applications. Consequently, these pros and cons have led EV battery manufacturers to lean more toward either of the predominant chemistries with a different mix of elements. This has led to various EV companies using LFP batteries in affordable and base-level versions of their EVs while utilizing NMC batteries in top-end or ‘sport’ versions of their EVs.
Reports suggest that EVs are less prone to catch fire compared to Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) vehicles, as well as hybrid vehicles.
However, EV batteries or Li-ion batteries, due to their high energy density, may experience relatively more rapid and hard-to-control fires than ICE or hybrid vehicles. This is also why EV fire incidents have gained significant public attention while conventional vehicle fire incidents are relatively low-profile.
LFP batteries are preferred for their high number of life cycles, reliability, cost-effectiveness, and safety. These types of batteries are relatively more stable than NMC batteries and have a wider optimal temperature range than NMC batteries, between 0°C and 45°C (32°F and 113°F). LFP varieties and types of batteries can withstand more charge and discharge cycles without significant degradation of capacity. LFP varieties and types of batteries predominant in India’s EV ecosystem are also less prone to thermal runaway, which is a phenomenon where a battery overheats and catches fire. This is ideal when considering India’s high temperatures in various states.
Thus, LFP batteries are more suitable for extreme climates and possess better safety features than NMC batteries. However, this disparity in safety between these two types of batteries is quickly being overcome with advances in Battery Management System (BMS) technology and other innovations in thermal runaway prevention and mitigation.
NMC batteries champion higher energy density, meaning that these electric vehicle batteries can pack more energy inside a smaller form factor. This allows them to deliver more power and range for EVs by reduced weight. These types of batteries are also more versatile and adaptable, as they can be customized to suit different applications by varying the ratio of nickel, manganese, and cobalt in the cathode. Globally, around 60% of EVs sold now contain NMC batteries.
Other than LFP and NMC, there are a few emerging battery technologies that are gaining traction in India. Some of them are:
Various sources confirm the dominance of LFP and NMC types of batteries in the Indian electric vehicle market, but they may have slightly varied projections for the future market share of these different types of electric vehicle batteries.
When EV batteries reach end-of-life in India, they are mandated by India’s Battery Waste Management Rules (BWMR 2022) to enter the battery recycling & repurposing stream, as part of Extended Producer Responsibility. Irrespective of the type of batteries; the size, form factor, or battery chemistry, LOHUM utilizes its proprietary NEETM™ technology to recycle them all to produce raw materials that are even higher in purity and performance than the materials that originally went into the battery.
In other words, the NEETM™ technology can recycle all the aforementioned types of batteries as it is fully chemistry-agnostic. This enables LOHUM to turn all types of Li-ion and electric vehicle batteries that have reached end-of-life, i.e. battery waste, into a source of sustainable secondary-ecosystem energy transition materials through recycling.
Stay tuned to the LOHUM blog and our LinkedIn page for more illuminating insights on battery energy, sustainability, types of batteries, energy transition, circular economy, battery reuse, 2nd life applications, Lithium-ion battery recycling, and more.
Related blogs
This entrepreneur wants India to make its own lithium-ion cells for electric vehicle batteries

Forbes India
Rajat Verma already recovers raw materials from used cells at his venture, LOHUM Cleantech. He wants to close the loop by making cells in India as well.
India needs integrated recycling and repurposing battery business model: Rajat Verma of LOHUM Cleantech

YOURSTORY
In an interaction with AutoStory, Rajat Verma, Founder and CEO of LOHUM Cleantech, speaks about building his company, and about battery manufacturing and repurposing as an industry.
Sourcing Raw Materials Is A Big Challenge In Li-ion Battery Space: Founder Lohum

Business World Disrupt
Recognized as ‘The Most Innovative Company of the year 2022’ by The Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), LOHUM is a producer of sustainable Li-ion battery raw materials
1800 572 8822
Email : enquiry@lohum.com
G98, Site, 5, Kasna, Block A, Surajpur Site V, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201306
LOHUM Cleantech Private Limited, Plot No. D-7 & 8, Site 5th, Kasna Industrial Area, Greater Noida, Gautam Budh Nagar, Uttar Pradesh – 201308
LOHUM Cleantech Private Limited, Plot No. O-17, Site 5th, Kasna Industrial Area, Greater Noida, Gautam Budh Nagar, Uttar Pradesh – 201308