India stands at a pivotal moment in its journey towards sustainable energy solutions. With the increasing demand for environmental protection, sustainability, and the imperative to reduce carbon emissions, the nation must pivot towards cleaner energy sources. In the pursuit of a sustainable and clean energy future, the importance of energy storage solutions cannot be overstated. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and growing demand for renewable energy, we find ourselves in need of innovative approaches to energy storage. One promising avenue that deserves significant attention and investment is the concept of second-life lithium battery energy storage solutions in India. This approach not only aligns with India’s ambitious goal of developing a 4 GWh worth Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) project by 2030 but also offers a multitude of benefits, from sustainable resource management to a more circular economy.
The drive towards a cleaner energy transition is intrinsically tied to the use of natural or renewable resources. In this context, second-life battery reuse has emerged as a critical stepping stone towards efficient and sustainable energy storage. But why is battery reuse before recycling such a vital aspect of India’s clean energy journey?
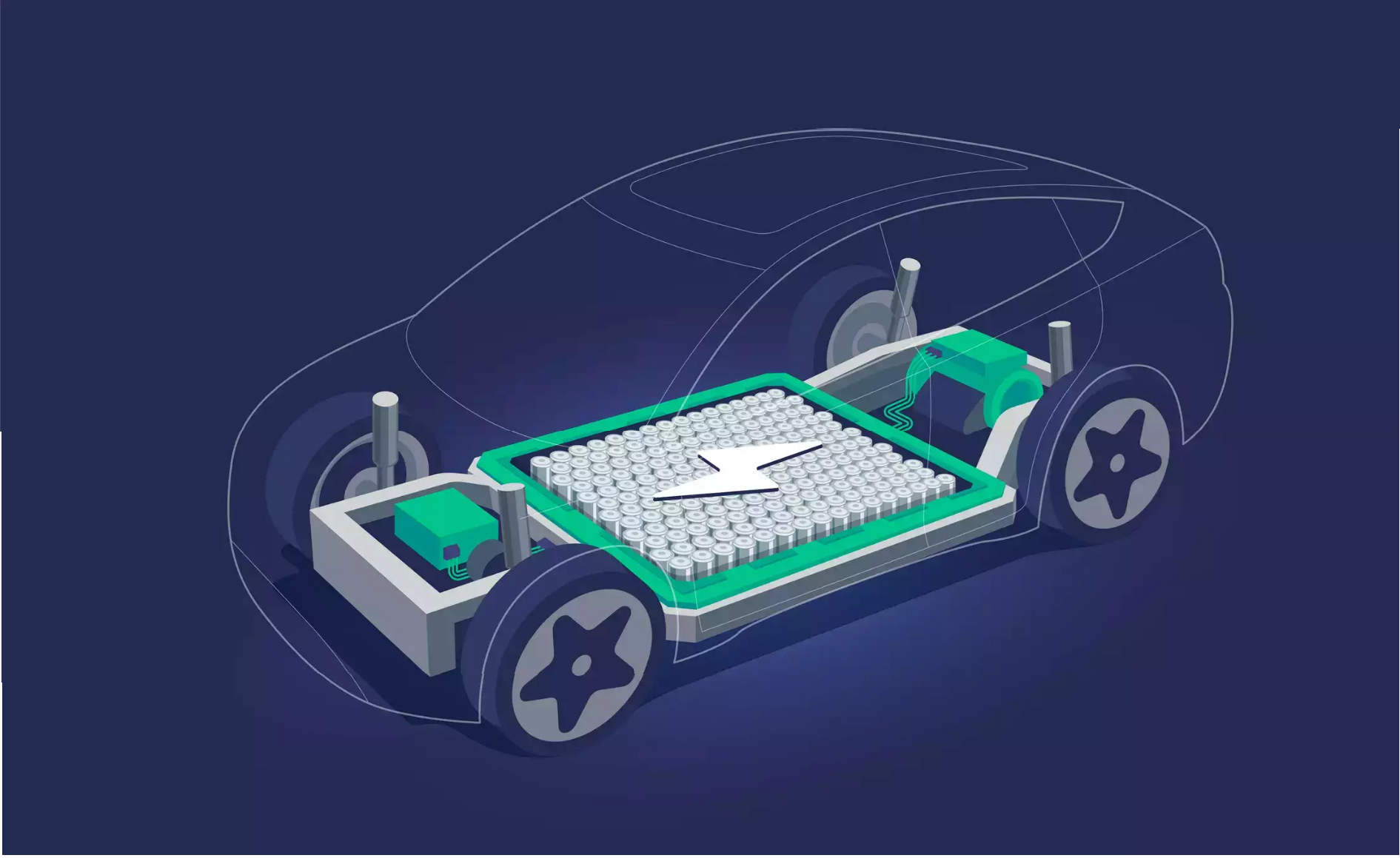
Lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy systems, have a finite life span. Over time, these batteries lose their capacity to hold a charge, making them unfit for their initial purposes. However, this doesn’t render them completely useless. The residual capacity of these batteries can be harnessed to create high-impact energy storage solutions, which can serve as a bridge to a more circular economy and cleaner energy grid.
One of the key drivers behind prioritizing battery reuse over immediate recycling is the preservation of valuable resources. Lithium-ion batteries are comprised of various materials, including lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are essential for their operation. Recycling these batteries involves breaking them down to recover these valuable materials, a process that consumes energy and has associated environmental costs.
By reusing these batteries in a second-life capacity, will maximize their utility and extend their lifespan, thus postponing the need for recycling. This means fewer new batteries need to be manufactured, reducing the demand for virgin resources and the associated environmental impact. Moreover, it reduces the pressure on the supply chain, making lithium-ion batteries more accessible and affordable for a broader range of applications.
From an environmental perspective, second-life lithium battery energy storage solutions represent a significant reduction in the carbon footprint of battery production. A study by the European Commission found that repurposing batteries can reduce their carbon footprint by up to 30% when compared to manufacturing new batteries from scratch. This reduction is primarily attributed to the fact that the production phase accounts for a substantial portion of a battery’s environmental impact.
In India, where the government is striving to make a significant shift towards green energy, the reuse of lithium-ion batteries can be a game-changer. According to the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, India aims to achieve a renewable energy capacity of 500 GW by 2030. Achieving such an ambitious target necessitates not only increasing renewable energy generation but also efficiently storing and managing that energy.
This is where second-life battery energy storage solutions come into play. As India expands its renewable energy infrastructure, there will be a growing need for energy storage solutions to manage the intermittency of sources like solar and wind power. High-quality, repurposed lithium-ion batteries can provide a cost-effective and sustainable way to meet this demand.
India is on the cusp of a transformative shift in its energy landscape. The government’s visionary National Framework 2023 for promoting energy storage systems signals a clear commitment to accelerating the adoption of cutting-edge technologies in the energy sector. This framework prioritizes the deployment of advanced energy storage solutions, including second-life battery storage, as a key component of India’s clean energy transition. The Government of India will provide substantial financial support up to 40 per cent of the capital cost in the form of Viability Gap Financing (VGF), marking an important milestone in the country’s ongoing commitment to environmental sustainability.
In recent years, the Indian government has implemented various schemes, including the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid &) Electric Vehicles (FAME) program, which encourages the adoption of electric vehicles and, by extension, the development of a second-life battery market. This commitment to sustainable energy solutions is commendable and can position India as a leading force in the global transition to clean energy and propelling the market for battery energy storage systems in India.
Therefore, to accelerate the adoption of high-impact second-life lithium battery energy storage solutions, it is imperative to bolster investment in this sector. Countries like EU and the United States have already made significant strides in this regard. The United States has implemented various incentives and subsidies to promote the development and deployment of energy storage technologies. The benefits of investing in second-life battery energy storage solutions are not limited to resource conservation and sustainable energy management. They extend to economic growth and job creation. As India endeavors to build a robust and competitive clean energy industry, investment in second-life battery solutions can stimulate economic activity, generate employment, and promote technological innovation.
By repurposing lithium-ion batteries and reducing the need for resource-intensive manufacturing, India can play a significant role in reducing global greenhouse gas emissions. Hence, realizing the full potential of second-life lithium battery energy storage solutions necessitates a concerted effort by both the public and private sectors. By doing so, India not set the stage for a cleaner future but also set an example for the world to follow.
Note: The author Rajat Verma is Founder & CEO of LOHUM Cleantech Pvt. Ltd.

Forbes India
Rajat Verma already recovers raw materials from used cells at his venture, LOHUM Cleantech. He wants to close the loop by making cells in India as well.

YOURSTORY
In an interaction with AutoStory, Rajat Verma, Founder and CEO of LOHUM Cleantech, speaks about building his company, and about battery manufacturing and repurposing as an industry.

Business World Disrupt
Recognized as ‘The Most Innovative Company of the year 2022’ by The Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), LOHUM is a producer of sustainable Li-ion battery raw materials
1800 572 8822
Email : enquiry@lohum.com
G98, Site, 5, Kasna, Block A, Surajpur Site V, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201306
LOHUM Cleantech Private Limited, Plot No. D-7 & 8, Site 5th, Kasna Industrial Area, Greater Noida, Gautam Budh Nagar, Uttar Pradesh – 201308
LOHUM Cleantech Private Limited, Plot No. O-17, Site 5th, Kasna Industrial Area, Greater Noida, Gautam Budh Nagar, Uttar Pradesh – 201308